Date: 7 February 2014
Image B
Copyright:
Dr D Denning, Wythenshawe Hospital, Manchester.(© Fungal Infection Trust)
Notes:
Patient BC
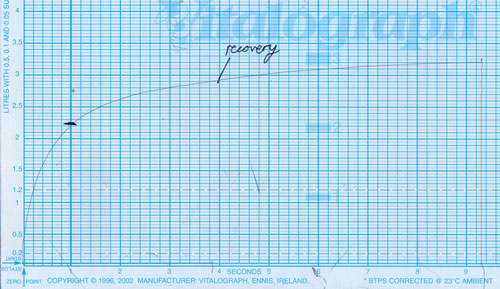
A petite women in her 50’s with severe asthma and fungal sensitization (SAFS) had been unable to tolerate either itraconazole or voriconazole for any length of time, and was severely disabled with her symptoms. One treatment option which is occasionally helpful is to give nebulised amphotericin B (link to video of Helen). She was given 10mg of amphotericin B deoxycholate in water through a Pari LC nebulizer, supervised by a senior physiotherapist. Shortly after starting this, she felt much more breathless and the nebulizer was stopped. Salbutamol rescue was administered. After about 40 minutes she recovered.
The spirometer readings show a starting FEV1 of 2.35 L/sec. This fell to 1.05 L/sec, a dramatic fall with amphotericin B nebulisation. (Image A) She recovered with salbutamol to 2.25 L/sec. (Image B)
Images library
Showing 10 posts of 2574 posts found.
-
Title
Legend
-
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)

-
Light microscopical appearance of vessel thrombus showing fungal element within it (Haematoxylin and eosin, x400).

-
Medium power view (H&E) of lung tissue in patient with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in which many of the fungal hyphae are seen in cross section.
Pulmaonary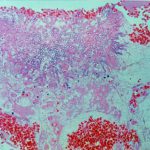
-
Light microscopical appearance of conidial head of A. fumigatus at an air interface in pulmonary tissue (Haematoxylin and eosin, x250).