Date: 26 November 2013
Fig3 Pulmonary artery
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Fig 1. Trachea and bronchi A 50+ year old woman received a double lung transplant for emphysema. She did well initially, but then Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from her airways, in association with mucous and a pseudomembrane covering parts of her anastomosis and airways. 2 months after her transplant she was undergoing bronchoscopy, and started to bleed. This rapidly became torrential and she suffered a cardiac arrest and died.
She underwent autopsy at which it was found that the larynx, trachea and major bronchi all contained blood (Fig 1).
The bronchial anastomoses were intact, but brown fluffy material was found overlying the stitches on both sides. On the right side plaques of similar material were seen distal to the anastomoses, overlying an ulcer and an obstructing the smaller bronchi.
On the left side an ulcer 1.5cm in diameter (with blood in it) was seen in the main bronchus distal to the anastomosis on the anterior wall (Fig 2). The sutures of the anastomosis are intact. The centre of the ulcer had ulcerated through into the left main pulmonary artery (Fig 3). The pulmonary artery shows necrosis and discolouration of the intimal surface over an area of 1.5-1.0cm.
Histopathology examination showed fungal hyphae perforating the bronchial wall and arterial wall around and in the ulcer. The ulcer on the right side showed hyphae perforating the wall and bronchial cartilage.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
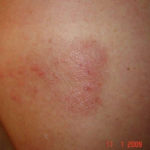
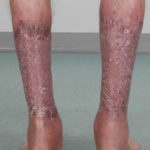
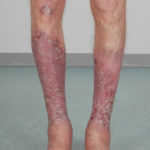
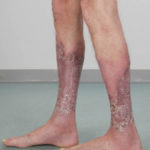
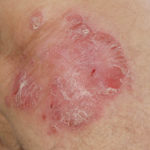
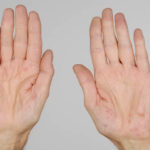
After 3 weeks of posaconazole given for chronic pulmonary aspergillosis, patient NC had a remarkable exacerbation of psoriasis. He had had psoriasis for years, with little trouble and almost no treatment. After taking posaconazole 400mg twice daily, he developed psoriatic plaques on his hands for the first time ever. The plaques on his lower legs became confluent. This occurred in association with worsening chest symptoms, notably increased coughing, more breathlessness and increasing oxygen requirement.
Posaconazole was stopped after 3 weeks, and 2 weeks later he was still very symptomatic with his chest. This responded to a 2 week course of corticosteroids, and his psoriasis also improved.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
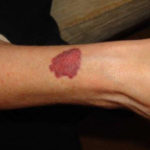
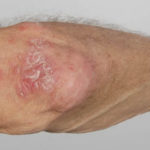
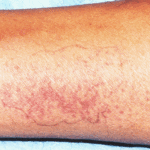
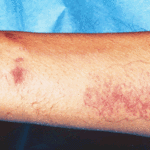
Patient PC: An example of localised caspofungin rash and phlebitis related to caspofungin infusion.
 ,
, 
-
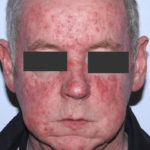
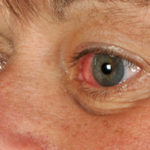
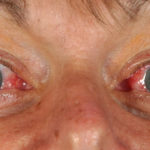
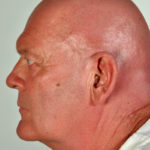
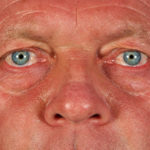
This 55 year old man with asthma, ABPA, severe bronchiectasis and lung fibrosis was treated with voriconazole, starting in June 2010. He had developed increasing dyspnoea on itraconazole for over 7 years, and his total IgE remained at 1100 KIU/L. He had marked photopsia (visual hallucinations) and facial erythema in the first 3 weeks of therapy. His trough voriconazole concentration was 1.17 mg/L. Over 3 months, he had minor improvement in his breathlessness but continued facial erythema, despite factor 50 sunblock. After 5 months of therapy his facial rash has altered to show acneiform lesions with localised crusting and background severe erythema. His face effectively crusted over, and he stopped therapy.
Over the next 3 weeks his facial appearance slowly improved .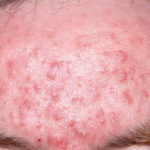 ,
,  ,
,