Date: 26 November 2013
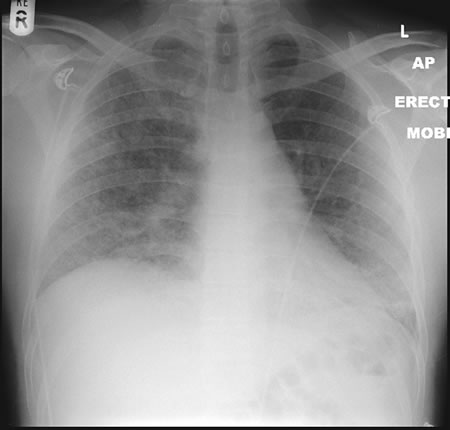
22/09/08 This chest radiograph shows bilateral hazy diffuse airspace disease predominating in the lower lungs with subtle nodularity in upper zones.
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
A 33 year old known Chronic Granulomatous Disorder (CGD) male presented to A&E in respiratory distress and admitted with severe bibasal pneumonia. He had been laying mulch in his garden. He had not been taking any prophylactic antifungal agents. Oxygen therapy was commenced in conjunction with IV bacterial and fungal treatment with Amphotericin B (Fungizone ®). Further consultation and an adverse reaction to the administration of Fungizone ® led to a switch to IV Voriconazole 300mg BD. The patient tested positive for aspergillus antibodies in serum. The patient declined a bronchoscopy, responded well to IV voriconazole and was discharged home 2 weeks post admission on maintenance voriconazole.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
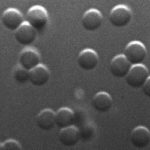
Test for aflatoxin B1. Standard curve wells in triplicate – columns 9, 10 & 11 – laid out horizontally. Triplicates of 14 samples laid out vertically in rows 2 to 8

-
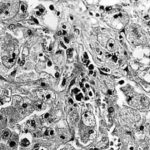
Light microscopical appearance of hepatic tissue in outbreak of aflatoxicosis showing centrilobular degeneration of hepatocytes with vacuolated cytoplasm and apoptoses (top right abnormal)(Haematoxylin and eosin).
-
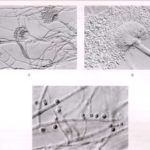
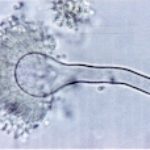
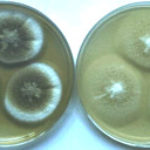
Aspergillus terreus Thom. A Colonies on MEA after one week; B detail of colony showing columnar conidial heads x 44 ; C conidial heads and tip x 920; D conidia x2330
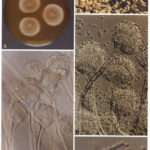
-
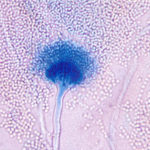
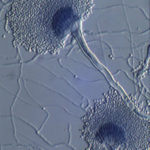
Aspergillus terreus Thom. Conidial head of Aspergillus terreus. Conidial heads are compact, columnar and biseriate. Conidiophores are hyaline to slightly yellow and smooth walled.