Date: 26 November 2013
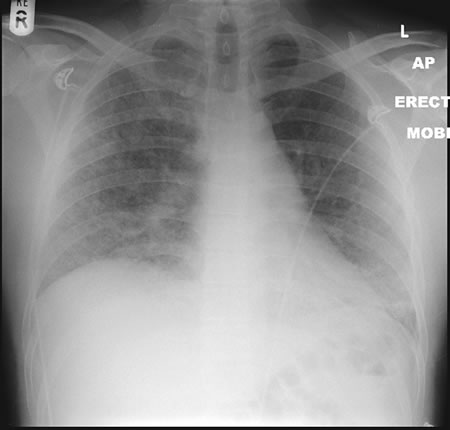
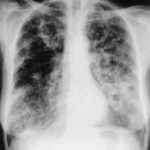
22/09/08 This chest radiograph shows bilateral hazy diffuse airspace disease predominating in the lower lungs with subtle nodularity in upper zones.
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
A 33 year old known Chronic Granulomatous Disorder (CGD) male presented to A&E in respiratory distress and admitted with severe bibasal pneumonia. He had been laying mulch in his garden. He had not been taking any prophylactic antifungal agents. Oxygen therapy was commenced in conjunction with IV bacterial and fungal treatment with Amphotericin B (Fungizone ®). Further consultation and an adverse reaction to the administration of Fungizone ® led to a switch to IV Voriconazole 300mg BD. The patient tested positive for aspergillus antibodies in serum. The patient declined a bronchoscopy, responded well to IV voriconazole and was discharged home 2 weeks post admission on maintenance voriconazole.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
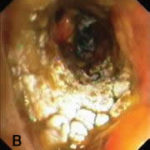
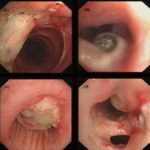
Bronchoscopic manifestations of Aspergillus tracheobronchitis. (a) Type I. Inflammatory infiltration, mucosa hyperaemia and plaques of pseudomembrane formation in the lumen without obvious airway occlusion. (b) Type II. Deep ulceration of the bronchial wall. (c) Type III. Significant airway occlusion by thick mucous plugs full of Aspergillus without definite deeper tissue invasion. (d) Type IV. Extensive tissue necrosis and pseudomembrane formation in the lumen with airway structures and severe airway occlusion (Wu 2010).
-
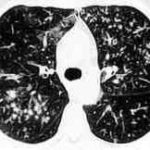
High resolution CT showing centrilobular nodular opacities and branching linear opacities (tree-in-bud appearance) (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
Chest X-ray showing poorly defined bilateral nodular opacities (Al-Alawi 2007).
-
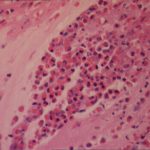
Gross pathologic specimen from autopsy shows the bronchial lumen covered by multiple whitish endobronchial nodules (arrows) (Franquet 2002).

-
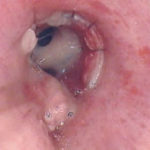
Invasive tracheobronchitis showing numerous nodules seen during bronchoscopy (Ronan D’Driscoll).

-
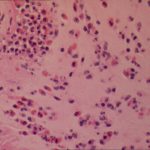
Pseudomembranous seen overlying the bronchial mucosa (Tasci 2006).