Date: 26 November 2013
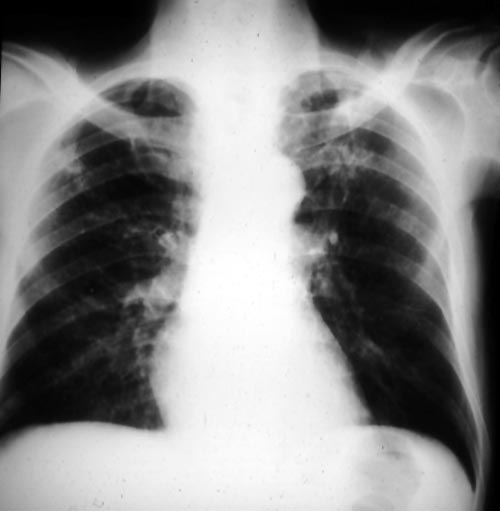
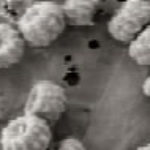
Bilateral upper-lobe cavities in AIDS, pt PC
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
This patient, thought initially to have pulmonary aspergillosis in AIDS, has bilateral upper-lobe cavities, more marked on the left. He presented with fever, nonproductive cough and dyspnoea. Bronchoscopy yielded Aspergillus fumigatus. He refused therapy and died with progressive disease. He is reported as patient 8 in Denning DW, Follansbee S, Scolaro M, Norris S, Edelstein D, Stevens DA. Pulmonary aspergillosis in AIDS. N Engl J Med 1991; 324: 654-662.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
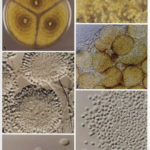
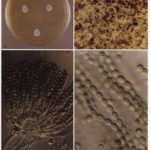
Pigmentation of Aspergillus versicolor colonies ranged from pale green to greenish-beige, pink-green, dark green and brown. Reverse is usually reddish. The growth rate is usually slow. Cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar with chloramphenicol.

-
A Colonies on MEA after one week; B, C conidial heads with tip of conidiophire, x920; D conidial head, x 2330; E conidial heads x920
![aspvers[2] aspvers2](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/aspvers2-150x150.jpg)
-
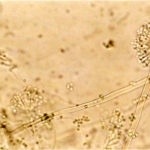
A Colonies on MEA + 20% sucrose after one week; B detail of colony showing columnar conidial heads x 44 ; C conidial heads x 920; D conidia x2330
-
Cultures are grown on malt extract agar for 5-7 days at 30°C.
Light microscopy-1000x stained with lacto-phenol and cotton blue.
-
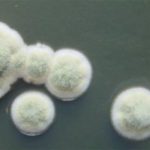
A Colonies on MEA +20% sucrose after one week; B ascomata x 40; C conidiophores x 920; D ascospores x2330; E ascoma x 230; F portion of ascoma with asci and ascospores, x 920.