Date: 26 November 2013
Patient MD with kyphoscoliosis and chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis and an aspergilloma. Patient exhibited azole resistant A. fumigatus.
Further details
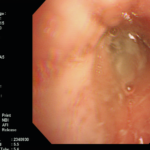
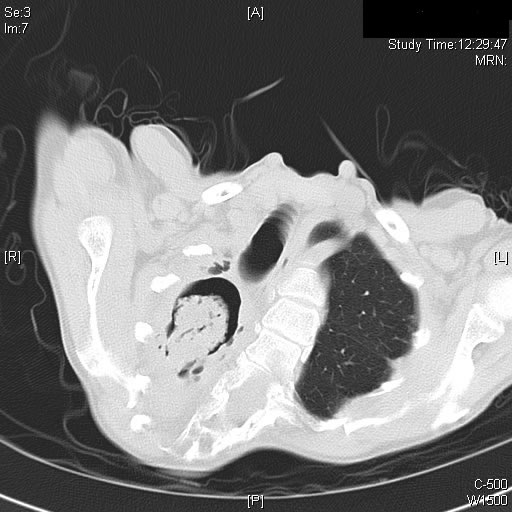
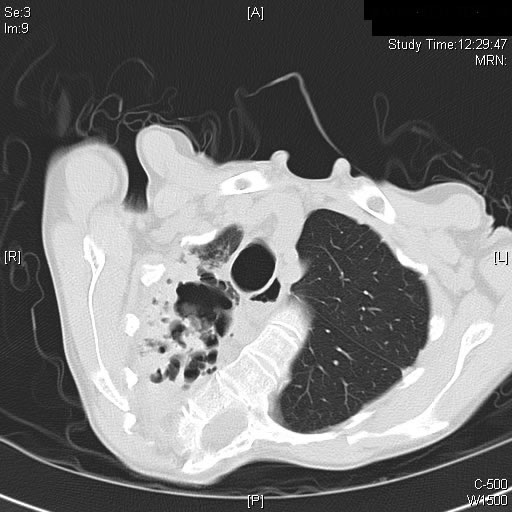
Image A. This CT scan cut shown shows a grossly distorted thorax because of the kyphoscoliosis, a nearly normal appearing left lung, her trachea at an odd angle, demonstrating the normal cartilage rings and an aspergilloma in a cavity which has replaced the right upper lobe. The cavity is surrounded by significant pleural thickening and fibrosis.
Image B. The other cut (slightly inferior) shows a complex large cavity and some smaller ones posteriorly, with some material consistent with a fungal ball within the large cavity. There is a separate cavity anteriorly and small air spaces within the extensive pleural thickening. Her trachea is widened. the left lung appears normal.
This patient with repaired juvenile scoliosis first recognised that she had pulmonary aspergillosis when she coughed up large amounts of blood, she was admitted to ICU and underwent bronchial artery embolisation, followed by tranexamic acid orally. A. fumigatus was cultured from sputum. A diagnosis of chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis with an aspergilloma was made. She didn’t improve with itraconazole (no fall in Aspergillus precipitins and continuing symptoms, despite good blood levels) and was treated with voriconazole. She had a good sympomatic response, with marginal improvement in her Aspergillus precipitins titre. Remission continued for over 3 years but then her symptoms of cough and general fatigue returned. Her sputum grew A. fumigatus again, which had MICs to itraconazole (>8 mg/L, resistant), voriconazole (8mg/L, resistant) and posaconazole (2mg/mL, resistant). She is being treated with amphotericin B.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
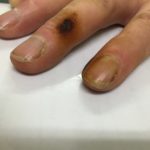
Patient with chronic productive cough, chest pain and ABPA, unable to take itraconazole or nebulised amphotericin B. Smokes at least 40 roll up cigarettes a day.
 ,
, 
-
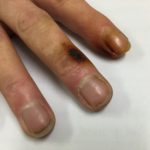
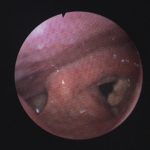
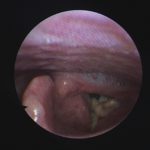
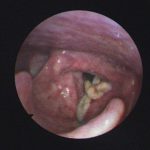
Laryngeal aspergillosis, probably related to inhaled corticosteroids.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
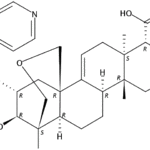
VL-2397 (formerly known as ASP2397) is a novel antifungal drug initially developed by our partner, Astellas Pharma. This drug was isolated from a leaf litter fungus Acremonium species collected in a Malaysian national park. Astellas presented two posters at the 2014 ICAAC meeting which described the in vitro and the in vivo antifungal activities of this drug. The differentiating attributes from the preclinical data of VL-2397 include:
- A novel mechanism of action, with a potential to be complementary or synergistic with the existing classes of antifungals.
- Rapid fungal cell kill activity demonstrated in preclinical models, which was faster than marketed antifungals.
- Activity against azole-resistant fungal species.
- Low propensity for P450 drug-drug interactions.
-
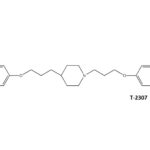
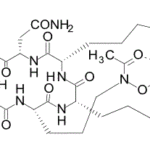
SCY-078, new orally available beta-1,3-d-glucan synthase inhibitor, Formely MK-3118.
-
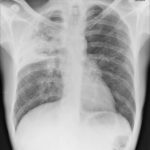
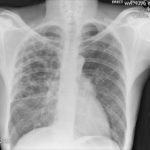
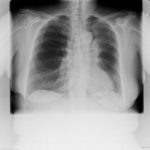
Pt DSM Community acquired primary Aspergillus pneumonia. Two x-rays taken on 02/02/2010 then 05/03/2010
 ,
, 

 ,
,