Date:
Copyright:
National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 102060393, Austalide C. Retrieved August 1, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Austalide-C.
Notes:
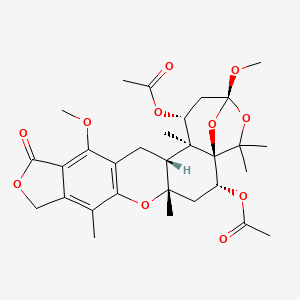
Structure of Austalide C
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Further details
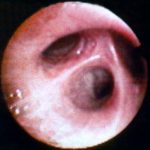
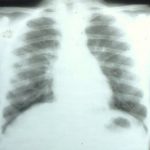
Image G. Patient was a 9 year old girl 5 months post matched unrelated donor (MUD) bone marrow transplantation with T-cell depletion, with reduced respiratory function (dyspnoea), cough and crackles at the bases, without fever. Donor and recipient were CMV antibody negative. 5/10/98.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
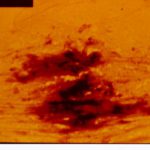
Fluorescence microscopy was performed on the same sample as blankophor® staining according to Ruchel R. & Margraf S. 1993, Mycoses 36, 239-242. The artefactual staining of fibres and cellular elements is due to previous drying of the smear and recedes with time.
-
A needle biopsy of a solitary round infiltrate found near the thoracic wall in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia was gram-stained and then treated with an alkaline solution of the whitening agent Blankophor®.

-
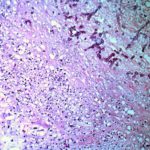
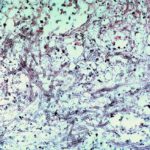
Medium power view (H&E) of cerebral abscess in which there are hyphae consistent with Aspergillus. Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from adjacent tissue.
-
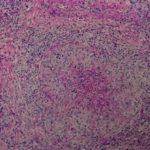
Medium power view (GMS) of kidney invaded by Aspergillus. The walls of the hyphae stain black. There are plentiful fungal hyphae within two glomeuli and there is also fungal invasion of adjacent cortical interstitial tissue.
-
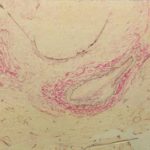
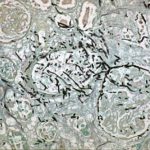
High power view (H&E) of uniform septate hyphae which show typical diclotomous branding characteristic of Aspergillus taken from mitral valve vegetation in a patient with disseminated aspergillosis. The hyphae are present within a background of fibrinous material.
-
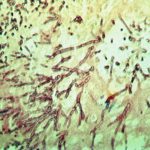
Medium power view (H&E) of lung tissue in patient with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in which many of the fungal hyphae are seen in cross section.
-
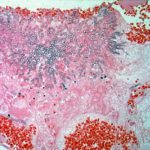
Medium power view of lung (H&E) in which there is invasion of lung parenchyma by hyphae characteristic of Aspergillus resulting in lung tissue infarction.