Date: 26 November 2013
This recording of peak flow was taken prior to and during the first 4 weeks of inhaled steroids (Becotide 100 and Duovent both 2 puffs 4x daily). The patient had had asthma since age 4, and been treated with bronchodilators and oral courses of steroids when severely affected. The chart, which the patient completed at home, shows that early in week one her peak flow varied from 200-250 L/min. As the medication started to work, the peak flows gradually increased to reach 360-420 L/min in the 4th week. The lower value each morning is characteristic of asthma.
The response to steroids is important confirmation of the diagnosis of asthma (reversible airways obstruction). Many years later she developed ABPA, while on inhaled steroids, with severe upper lobe central bronchiectasis, an IgE of 6,800 Kiu/L, positive aspergillus precipitins, an Aspergillus RAST of 58.7KUa/L (normal <0.4) and eosinophilia.
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
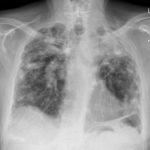
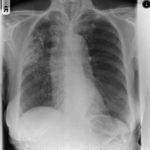
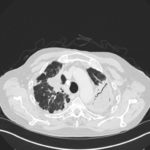
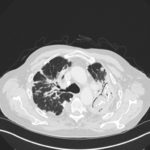
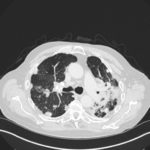
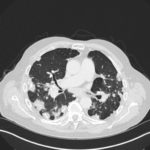
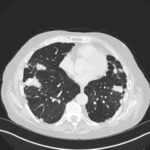
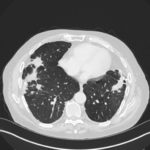
Mr RM is 80 and an ex-coal miner.He developed pneumoconiosis from exposure to coal dust. He also developed rheumatoid arthritis and the combination of this disease and pneumoconiosis is called Caplan’s syndrome.
His chest Xray in early 2015 shows extensive bilateral pulmonary shadowing with solid looking nodules superimposed on abnormal lung fields, contraction of his left lung with an elevated diaphragm and a large left upper lobe aspergilloma, displaying a classic air crescent. His CT scan from mid 2014 demonstrates a large aspergilloma in a cavity on the left, with marked pleural thickening around it, which is partially ‘calcified’ towards its base. Inferiorly on other images,remarkable pleural thickening and fibrotic irregular and spiculated nodules are seen, most partially calcified.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,