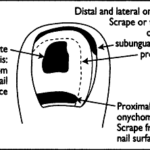
Date: 7 May 2013
Copyright:
Copyright B.Flannigan, R Samson & JD Miller (From Microorganisms in home and indoor work environments, Published by Taylor and Francis)
Notes:
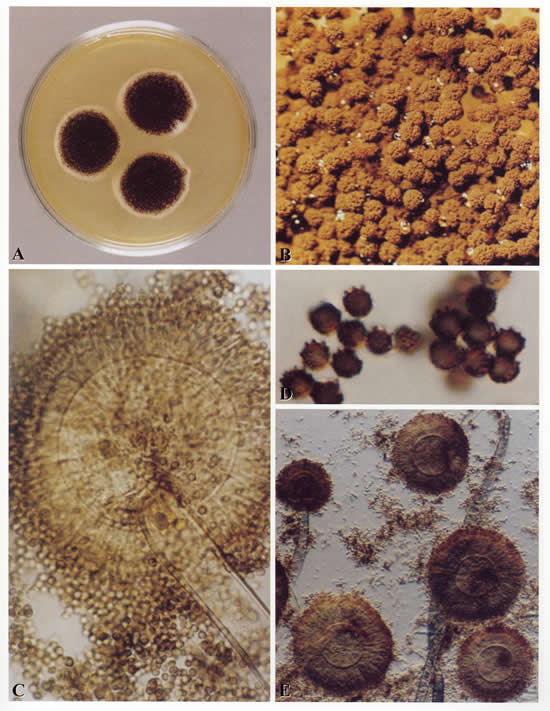
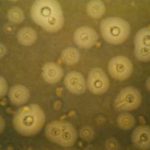
Colonies on CYA 60 mm or more diam, usually covering the whole Petri dish, plane, velutinous, of low, usually subsurface, white mycelium, surmounted by a layer of closely packed, black conidial heads, ca 2-3 mm high; reverse usually pale, sometimes pale to bright yellow. Colonies on MEA varying from 30-60 mm diam, usually smaller than those on CYA and often quite sparse by comparison, otherwise similar. Colonies on G25N 18-30 mm diam, plane, velutinous, with white or pale yellow mycelium visible at the margins, otherwise similar to those on CYA; reverse pale or occasionally with areas of deep brown. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies 60 mm or more diam, covering the available space, sometimes sulcate, otherwise similar to those on CYA at 25°C.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, 1.0-3.0 mm long, with heavy, hyaline, smooth walls; vesicles spherical, usually 50-75 µm diam, bearing closely packed metulae and phialides over the whole surface; metulae 10-15 µm long, or sometimes more; phialides 7-10 µm long; conidia spherical, 4-5 µm diam, brown, with walls conspicuously roughened or sometimes striate, borne in large, radiate heads.
Distinctive features
One of the best known of all fungal species, Aspergillus niger is distinguished by its spherical black conidia, derived from colonies which show little or no other colouring.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
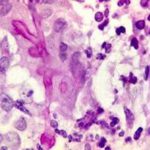
BAL specimen showing hyaline, septate hyphae consistent with Aspergillus, stained with Blankophor

-
Mucous plug examined by light microscopy with KOH, showing a network of hyaline branching hyphae typical of Aspergillus, from a patient with ABPA.

-
Corneal scraping stained with lactophenol cotton blue showing beaded septate hyphae not typical of either Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp, being more consistent with a dematiceous (ie brown coloured) fungus
-
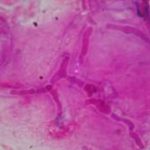
Corneal scrape with lactophenol cotton blue shows separate hyphae with Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp.
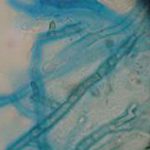
-
A filamentous fungus in the CSF of a patient with meningitis that grew Candida albicans in culture subsequently.

-
Transmission electron micrograph of a C. neoformans cell seen in CSF in an AIDS patients with remarkably little capsule present. These cells may be mistaken for lymphocytes.
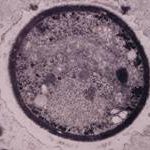
-
India ink preparation of CSF showing multiple yeasts with large capsules, and narrow buds to smaller daughter cells, typical of C. neoformans