Date: 26 November 2013
Biofilms on bronchial epithelial cells in vitro.
Copyright:
Images kindly donated by Frank-Michael C. Müller, Pediatric Pulmonology, Cystic Fibrosis Centre and Infectious Diseases, Department of Pediatrics III, University of Heidelberg, Im Neuenheimer Feld 430, D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany.
Notes:
Confocal scanning laser microscopy (CLSM), using CAAF(green) Fun1(red) stained biofilm. The red color of the FUN 1 cell stain was localized in dense aggregates in the cytoplasm of metabolically active cells. Thus, areas of red fluorescence represented metabolically active cells, and green fluorescence indicated cell wall-like polysaccharides, while yellow areas represented dual staining.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
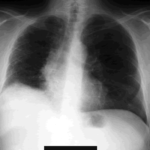
The chest x-ray shows a patient who had a left lung transplanted in May 2003 for cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis, which was diagnosed post-transplant as sarcoidosis.
-
Gross pathology demonstrating the great pleural thickness and two cavities (upper lobe and superior segment of lower lobe) with fragments of fungal mass.

-
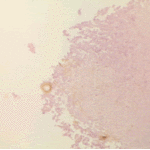
Histopathological appearance of a fungus ball. Note a conidial head resulting from fungal exposure to the air.
-
Histopathological appearance of a fungus ball caused by Scedosporium apiospermum. The presence of anneloconidia differentiates it from Aspergillus.

-
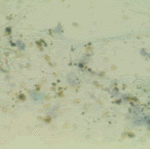
Chronic necrotising aspergillosis. Hyaline hyphal and calcium oxalate crystals obtained by needle aspirate biopsy from a diabetic patient with chronic necrotizing aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus niger (Papanicolaou, x 100).
-
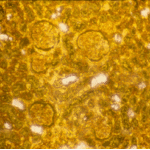
Aspergillus niger fungus ball and acute oxalosis. Higher magnification of adjacent replicate section.
-
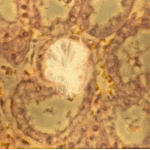
Oxalate crystals within renal tubuli (H&E, phase contrast, x 100). This patient developed acute oxalosis.
-
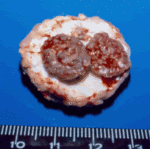
Lung surface. Fungus ball, severe parenchymal fibrosis and pleural thickening.



 ,
, 
 ,
,  ,
, 