Date: 7 May 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
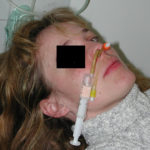
Yamik catheter for rinsing nasal and paranasal cavities. Image C
-
Yamik catheter for rinsing nasal and paranasal cavities. Image B
-
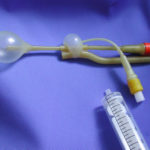
Yamik catheter for rinsing nasal and paranasal cavities. Image E
-
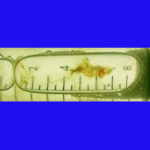
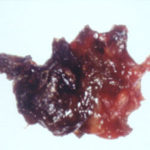
Patient with allergic fungal sinusitis. Eosinophilic mucin with A. flavus in the nasal cavity. Irregular crust of 2.5 cm from a patient diagnosed as allergic fungal sinusitis.
-
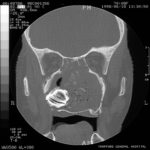
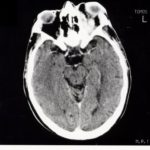
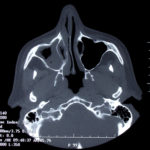
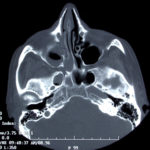
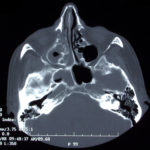
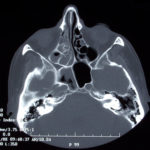
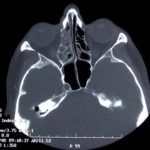
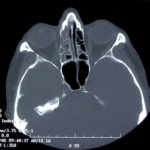
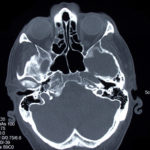
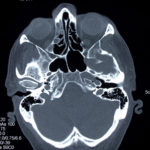
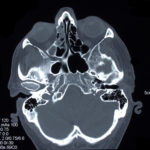
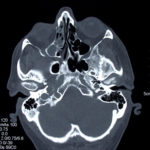
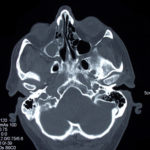
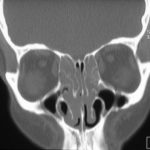
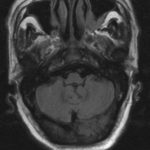
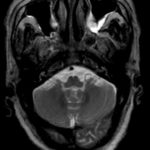
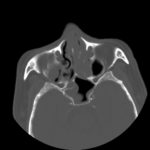
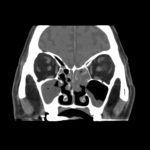
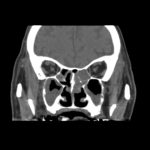
This patient was diagnosed with Myelodyspasia/ Acute Myeloid Leukaemia in January 05. When he received intensive chemotherapy. Had previous history of chronic sinusitis, but after chemotherapy he developed significant maxillary sinusitis. He was treated with Caspofungin with good response, and subsequently with voriconazole. Patient has further CT scans in August 05 with myelodysplasia in remission.
A biopsy of ethmoid sinus in May showed a chronic inflammmatory process with bony invasion by fungal hyphae. The patient was in remission from myelodysplasia and was not undergoing treatment for this at the time of the scans.
In Aug 05 scans show the right maxillary sinus is now opacified. Destruction of superior medial wall of right maxillary sinus. Superiorly there was bone destruction with communication with the lower right ethmoid air cells. Lateral wall of right maxillary sinus remains thick walled with irregular periosteal thickening. No significant abnormality is seen within the nasal cavity or left paranasal sinuses. The biopsy of the ethmoid sinus revealed hyphae consistent with aspergillus. Since the patient was on voriconazole at this time this may indicate resistance. The case is ongoing with further surgery for debridement of right nasal side imminent. The patient is currently in remission.
Feb 06 D Denning
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
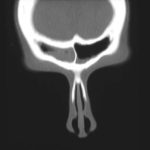
This 33 year old woman with severe asthma since childhood and recent nasal obstruction, who did not fulfil the criteria for ABPA, had evidence of skin test sensitisation to Aspergillus. Itraconazole therapy orally improved her pulmonary symptoms and allowed a substantial reduction in the need for oral steroids and inhaled steroids. Nasal polyposis improved slightly, but she still required polypectomy and nasal steroids.
 ,
, 

![Asp[1]fumighead2copyr Asp[1]fumighead2copyr](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Asp1fumighead2copyr.jpg)
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,