Date: 7 May 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Nasal aspergillosis in an English Pointer. Photograph of an English Pointer with nasal aspergillosis
Nasal aspergillosis in an English Pointer. Photograph of an English Pointer with nasal aspergillosis

-
Domestic crossbred cat with disseminated aspergillosis. Diff Quik stained squash preparation of material obtained from thoracotomy of a 3 year old domestic crossbred cat with invasive Aspergillus fumigatus infection. The cat had marked enlargement of the hilar lymph nodes that resulted in a partial tracheal obstruction. This smear was made from portions of the hilar lymph node resected at thoracotomy. Magnification x 132.
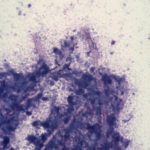
-
English Pointer with nasal aspergillosis. Diff Quik stained cytological smear of material obtained from the frontal sinus of a 7 year old English Pointer with nasal aspergillosis. This infection was caused by Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal hyphae are beautifully demonstrated by the Diff Quik stain. Magnification x 200.

-
Nasal aspergillosis in a Schnauzer. Histological section of fungal plaques removed surgically from the frontal sinus of a 5 year old Schnauzer with nasal aspergillosis. This infection was caused by Aspergillus fumigatus. H & E; x 200.

-
Disseminated aspergillosis in a German Shepherd. Masses of fungal hyphae in the renal pelvis of both kidneys in a young German Shepherd dog with disseminated Aspergillus terreus infection.
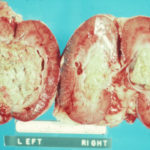
-
Nasal aspergillosis. KOH preparation of fungal plaques surgically removed from the frontal sinus of a Schnauzer with nasal aspergillosis due to Aspergillus fumigatus.
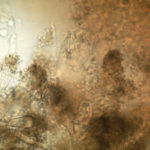
-
English Pointer with nasal aspergillosis. English Pointer with nasal aspergillosis treated by topical enilconazole injected through surgically inserted indwelling plastic tubes.

-
German Shepherd with disseminated aspergillosis. Unilateral pyelonephritis in a German Shepherd dog with disseminated Aspergillus terreus infection.
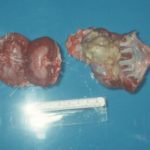
-
Rottweiler treated with indwelling plastic tubes. Photograph of a Rottweiler crossbred dog treated with indwelling plastic tubes placed surgically into the nasal cavity and frontal sinuses.

-
Rottweiler crossbred dog with nasal aspergillosis. A Rottweiler crossbred dog with nasal aspergillosis due to Aspergillus fumigatus infection. Note the loss of pigment below the nostril on the worst affected side – this finding is suggestive of a diagnosis of chronic nasal aspergillosis in the dog.


![Asp[1]fumighead2copyr Asp[1]fumighead2copyr](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Asp1fumighead2copyr.jpg)