Date: 7 May 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Nasal, sinus and orbital aspergillosis in a cat. Frontal bone – less severe bone erosiondorsally over the rostral part of the frontal sinus
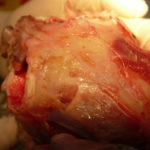
-
Nasal, sinus and orbital aspergillosis in a cat. Nose- severe bone erosion rostrally through the nasal bone.
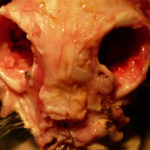
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Lesions found in captive Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) with aspergillosis as determined by histology.Hyaline, septate and branching hyphae, and asexual reproductive structure of Aspergillus observed in the tissues of Magellanic penguin with fatal aspergillosis. (PAS stain )
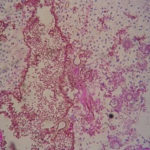
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Lesions found in captive Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) with aspergillosis as determined by histology. Hyaline, septate and branching hyphae, and asexual reproductive structure of Aspergillus observed in the tissues of Magellanic penguin with fatal aspergillosis. (Grocott’s stain)
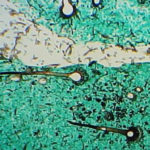
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Multiple granulomatous nodules at syrinx with necrotic debris and caseous exudates. These lesions were responsible for partial obstruction of the air passages.
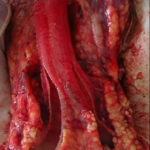
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Lesions found in captive Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) with aspergillosis as determined by histology. Larges masses formed by multiple nodules in the air sacs and in the adrenal gland.
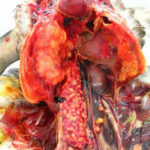
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Lesions found in captive Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) with aspergillosis as determined by histology.Adrenal gland involvement (adjacent to kidney) – characterized by massive enlargement to 8-10 cm, formed by multiple granulomatous nodules.

-
Aspergillosis in penguins Lesions found in captive Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) with aspergillosis as determined by histology.Adrenal gland involvement (adjacent to kidney) – characterized by massive enlargement to 8-10 cm, formed by multiple granulomatous nodules.
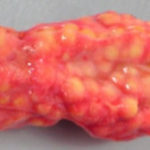
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Lesions found in captive Magellanic penguins (Spheniscus magellanicus) with aspergillosis as determined by histology.Adrenal gland involvement (adjacent to kidney) – characterized by massive enlargement to 8-10 cm, formed by multiple granulomatous nodules.
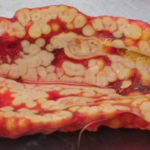
-
Aspergillosis in penguins. Multiple granulomatous nodules in the surface of the kidney


![Asp[1]fumighead2copyr Asp[1]fumighead2copyr](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Asp1fumighead2copyr.jpg)