Date: 7 May 2013
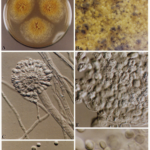
A four day A. fumigatus culture on malt extract agar (above). Light microscopy pictures are taken at 1000x mag., stained with lacto-phenol cotton blue (right).
Copyright:
With thanks to Niall Hamilton.
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
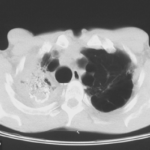
Diagnosis: Aspergilloma with invasive aspergillosis evidence of invasion found in the lumbar spine and brain, in addition to heart.
Fungal endocarditis with NO evidence of bacterial endocarditismia.Additional image details:
A. Normal chest X ray:
This (normal) chest X-ray was taken about 6 weeks before endocarditis was diagnosed, and 3 months before death due to disseminated aspergillosis. No CT scan was done (a chest radiograph has a 10% false negative rate in leukaemic patients, compared with CT).B. Aspergillus niger Fungal ball:
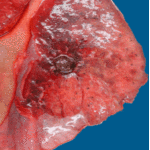
Gross section of lung at autopsy showing a discrete, well-demarcated dark/black mass surrounded by a fibrotic capsule. There was no evidence of local invasion, or infarction. The patient had had acute myeloid leukaemia (M1) and responded poorly to chemotherapy. He developed A.niger endocarditis and disseminated disease to the kidneys, lumbar disc and heart, probably arisiong from this lesion. It is unclear whether this lung lesion was a partially cured ‘mycotic lung sequestrum’ following antifungal therapy, or originated as an aspergilloma. The confirmation of genus and species was obtained by PCR on blood and vegetations.C. Endocarditis:
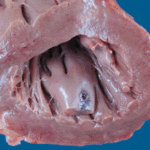
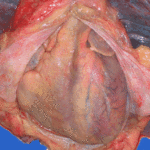
Macroscopic view of the heart at autopsy, showing an infracted lesion on the papillary muscle of the mitral valve in the left ventricle. In addition the patient had large vegetations, which are not shown here. The confirmation of genus and species was obtained by PCR on blood and vegetations; the pericarditis was a manifestation of disseminated aspergillosis.D. Pericarditis due to Aspergillus niger:
Macroscopic view of the pericardium at autopsy, showing gross chronic haemorrhagic pericarditis. The confirmation of genus and species was obtained by PCR on blood and vegetations; the pericarditis was a manifestation of disseminated aspergillosis.E. Lumbar discitis:
Macroscopic lesion of a lumbar intervertebral vertebral at autopsy, showing haemorrhagic necrosis, caused by hyphal invasion and infarction. The confirmation of genus and species was obtained by PCR on blood and vegetations; the discitis was a manifestation of disseminated aspergillosis.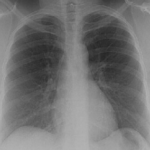 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
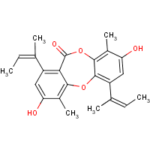
Secondary metabolites, structure diagram: Trivial name – Folipastatin

![Asp[1]fumighead Asp[1]fumighead](https://www.aspergillus.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/11/Asp1fumighead.jpg)