Date: 7 May 2013
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 40-60 mm diam, plane or lightly wrinkled, low, dense and velutinous or with a sparse, floccose overgrowth; mycelium inconspicuous, white; conidial heads borne in a continuous, densely packed layer, Greyish Turquoise to Dark Turquoise (24-25E-F5); clear exudate sometimes produced in small amounts; reverse pale or greenish. Colonies on MEA 40-60 mm diam, similar to those on CYA but less dense and with conidia in duller colours (24-25E-F3); reverse uncoloured or greyish. Colonies on G25N less than 10 mm diam, sometimes only germination, of white mycelium. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies covering the available area, i.e. a whole Petri dish in 2 days from a single point inoculum, of similar appearance to those on CYA at 25°C, but with conidial columns longer and conidia darker, greenish grey to pure grey.
Conidiophores borne from surface hyphae, stipes 200-400 µm long, sometimes sinuous, with colourless, thin, smooth walls, enlarging gradually into pyriform vesicles; vesicles 20-30 µm diam, fertile over half or more of the enlarged area, bearing phialides only, the lateral ones characteristically bent so that the tips are approximately parallel to the stipe axis; phialides crowded, 6-8 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, 2.5-3.0 µm diam, with finely roughened or spinose walls, forming radiate heads at first, then well defined columns of conidia.
Distinctive features
This distinctive species can be recognised in the unopened Petri dish by its broad, velutinous, bluish colonies bearing characteristic, well defined columns of conidia. Growth at 37°C is exceptionally rapid. Conidial heads are also diagnostic: pyriform vesicles bear crowded phialides which bend to be roughly parallel to the stipe axis. Care should be exercised in handling cultures of this species.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
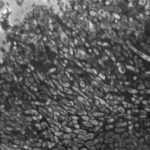
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (10x magnification)

-
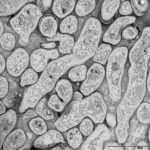
Light microscopic image of hyphae in an aspergilloma (400x magnification)
-
An aspergilloma (or fungal ball) is a mass of fungus found inside the body, for example inside cavities such as the lungs or sinuses, or as abscesses in organs such as the brain or kidney. They are made up of threadlike fungal strands (hyphae) that are densely packed but only around 1/200 of a millimetre in diameter. A mass of hyphae is called a mycelium.
In this image, a slice through an aspergilloma has been imaged using a transmission electron microscope.
-
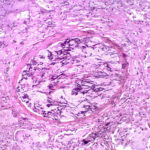
Aspergillus can punch through the lining of the lungs and invade the blood vessels below, in a process called angioinvasion. It can result in blockage (occlusion) of the blood vessel and damage to the local tissue through lack of oxygen (infarction). In severely immunocompromised patients, fragments can even break off and travel to other organs in the body.
In this image, a tissue section through a blocked blood vessel has been stained with the dyes haematoxylin (purple, binds DNA) and eosin (pink, binds proteins).
-
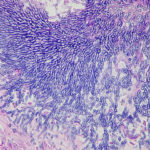
Showing the edge of a colony of aspergillus forming a fungal ball. The fungal hyphae exhibit dichotomous 45 degree angle branching and septae typical of Aspergillus.
-
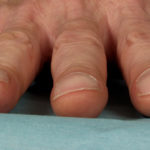
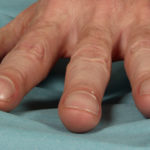
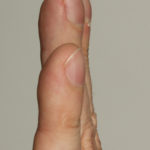
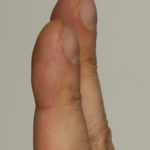
Pt CJ finger clubbing, this patient had chronic cavitary pulmonary aspergillosis, with an aspergilloma since 1988, following an episode of haemoptysis. Currently patient still has symptomatic disease.
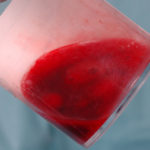
Images E,F Blood stained sputum samples from this patient.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x300. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).
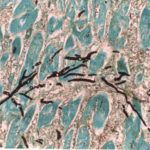
-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x150. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Disseminated, invasive aspergillosis showing dichotomously branching hyphae. Original magnification x50. Stained with Gomori Methenamine Silver (GMS).

-
Light microscopical appearance of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis showing vessel occlusion with thrombus and distal infarction (Haematoxylin and eosin, x100)


