Date: 26 November 2013
Aspergillus flavus
Copyright:
© Fungal Research Trust
Notes:
Colonies on CYA 60-70 mm diam, plane, sparse to moderately dense, velutinous in marginal areas at least, often floccose centrally, sometimes deeply so; mycelium only conspicuous in floccose areas, white; conidial heads usually borne uniformly over the whole colony, but sparse or absent in areas of floccose growth or sclerotial production, characteristically Greyish Green to Olive Yellow (1-2B-E5-7), but sometimes pure Yellow (2-3A7-8), becoming greenish in age; sclerotia produced by about 50% of isolates, at first white, becoming deep reddish brown, density varying from inconspicuous to dominating colony appearance and almost entirely suppressing conidial production; exudate sometimes produced, clear, or reddish brown near sclerotia; reverse uncoloured or brown to reddish brown beneath sclerotia. Colonies on MEA 50-70 mm diam, similar to those on CYA although usually less dense. Colonies on G25N 25-40 mm diam, similar to those on CYA or more deeply floccose and with little conidial production, reverse pale to orange or salmon. No growth at 5°C. At 37°C, colonies usually 55-65 mm diam, similar to those on CYA at 25°C, but more velutinous, with olive conidia, and sometimes with more abundant sclerotia.
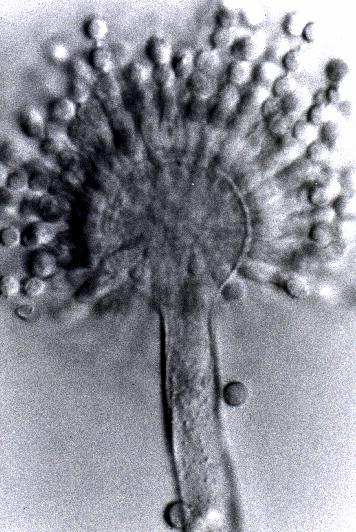
Sclerotia produced by some isolates, at first white, rapidly becoming hard and reddish brown to black, spherical, usually 400- 800 µm diam. Teleomorph not known. Conidiophores borne from subsurface or surface hyphae, stipes 400 µm to 1 mm or more long, colourless or pale brown, rough walled; vesicles spherical, 20-45 µm diam, fertile over three quarters of the surface, typically bearing both metulae and phialides, but in some isolates a proportion or even a majority of heads with phialides alone; metulae and phialides of similar size, 7-10 µm long; conidia spherical to subspheroidal, usually 3.5-5.0 µm diam, with relatively thin walls, finely roughened or, rarely, smooth.
Distinctive features
Aspergillus flavus is distinguished by rapid growth at both 25°C and 37°C, and a bright yellow green (or less commonly yellow) conidial colour. A. flavus produces conidia which are rather variable in shape and size, have relatively thin walls, and range from smooth to moderately rough, the majority being finely rough.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
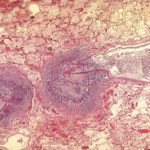
Medium power view of lung (H&E) in which there is invasion of lung parenchyma by hyphae characteristic of Aspergillus resulting in lung tissue infarction.
-
Vascular thrombosis. Medium power view (H&E) of a blood vessel occluded by fungal hyphae and thrombosis. Some fungal hyphae can be seen traversing the vessel wall.

-
Four colonies of Aspergillus on an agar plate containing rose bengal (to limit colony spending) and elastin fibres (light pink dots). Underneath and surrounding the colonies, the elastin fibres have gone, indicating enzymatic degradation

-
High power view of elastin fibres in an arterial wall being forced apart by Aspergillus hyphae. As Aspergillus is angiotropic and produces an elastase, it was uncertain how it traversed vessel walls. It appears to do so without any dissolution of elastin fibres.

-
Medium power view (GMS) of hyphae seen within an arterial wall which is characteristic of angioinvasive Aspergillus.

-
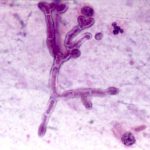
High power view (H&E) of a branching mould, consistent with Aspergillus inside a giant cell in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease.
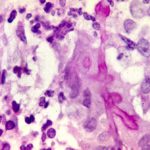
-
High power view (GMS) of an Aspergillus hypha within a giant cell in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease infected with Aspergillus.

-
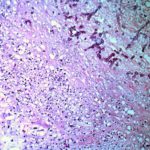
Medium power view (GMS) of the contents of a cerebral abscess in which there are hyphae typical of Aspergillus. Aspergillus fumigatus was grown from adjacent tissue.
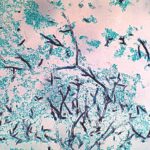
-
Low power view (H&E) showing a pulmonary vein and a small bronchus infiltrated by fungal hyphae with associated necrotising inflammation.