Date: 26 November 2013
History : A 20 yr old female with cystic fibrosis complicated by CF-related Diabetes mellitus (diagnosed at age 12 years) & ABPA (diagnosed at
15 years ). She was fairly stable until last 9 months, when she started to experience frequent pulmonary exacerbations, which have prompted intensive therapies.
Her serum IgE at the time of diagnosis was 5060 IU/L, skin prick test for aspergillus was positive, and serum was positive for precipitating antibodies to Aspergillus. She was treated with oral prednisone (1 mg/kg/day) for first two weeks followed by prednisone at 0.5 mg/kg every other day for at least 6 months with some clinical and serologic improvement. Over the following 5 years, she presented with a pattern of repeated episodic exacerbations with wheezing and crackles, increases in IgE and need to increase prednisone dosage. In an attempt to control her frequent ABPA relapses, itraconazole was added at 200mg twice a day, with some clinical & serologic improvement.
2-3 weeks prior to the scans and X rays, she developed severe protracted coughing spells associated with minor hemoptysis, low grade intermittent fever, and weight loss. Her FEV1 declined in a 3 months period from 56% to 33%.
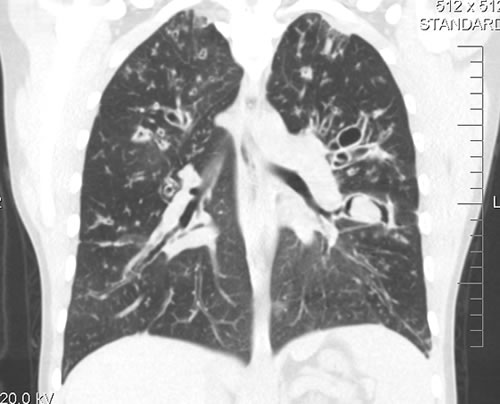
A chest-x ray (Fig 3) did not reveal any new changes when compared to the one obtained almost a year before. A CT scan of the chest Figs 1 and 2- lateral view), however shows an ovoid soft tissue density within an ectatic bronchi in the anterior basal segment of the LLL, felt to be an aspergilloma.
She was started on oral voriconazole (3 months after the above scans and X-rays) which is better absorbed in CF patients than itraconazole, at 200mg twice a day. Her prednisone was gradually reduced to 5 mgs/day and her FEV1 increased to 46% of predicted (03/31/10), her IgE level was 1167 kU/L (previously in January 2009, her IgE level was 3053 kU/L)and her weight has plateaued.
Since she was not fit enough for surgery at that time, removing the aspergilloma by flexible bronchoscopy was unsuccessful. The aspergilloma can be seen at bronchoscopy in Fig 4.
Go to follow up 12 months later
Copyright:
Kindly donated by Dr N Turcios, Director of pediatric pulmonology/cystic fibrosis in Somerville, NJ.
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
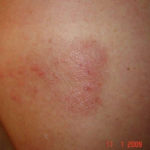
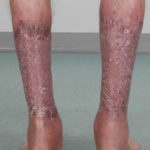
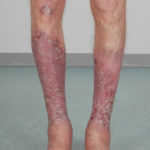
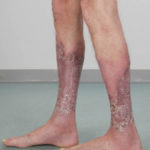
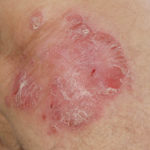
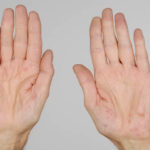
After 3 weeks of posaconazole given for chronic pulmonary aspergillosis, patient NC had a remarkable exacerbation of psoriasis. He had had psoriasis for years, with little trouble and almost no treatment. After taking posaconazole 400mg twice daily, he developed psoriatic plaques on his hands for the first time ever. The plaques on his lower legs became confluent. This occurred in association with worsening chest symptoms, notably increased coughing, more breathlessness and increasing oxygen requirement.
Posaconazole was stopped after 3 weeks, and 2 weeks later he was still very symptomatic with his chest. This responded to a 2 week course of corticosteroids, and his psoriasis also improved.
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ,
, 
-
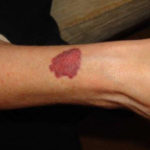
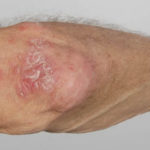
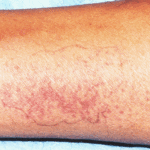
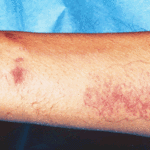
Patient PC: An example of localised caspofungin rash and phlebitis related to caspofungin infusion.
 ,
, 
-
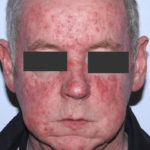
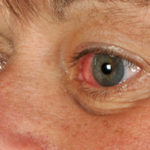
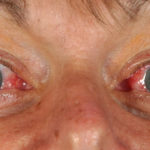
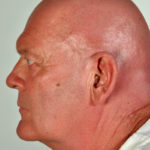
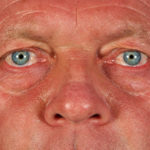
This 55 year old man with asthma, ABPA, severe bronchiectasis and lung fibrosis was treated with voriconazole, starting in June 2010. He had developed increasing dyspnoea on itraconazole for over 7 years, and his total IgE remained at 1100 KIU/L. He had marked photopsia (visual hallucinations) and facial erythema in the first 3 weeks of therapy. His trough voriconazole concentration was 1.17 mg/L. Over 3 months, he had minor improvement in his breathlessness but continued facial erythema, despite factor 50 sunblock. After 5 months of therapy his facial rash has altered to show acneiform lesions with localised crusting and background severe erythema. His face effectively crusted over, and he stopped therapy.
Over the next 3 weeks his facial appearance slowly improved .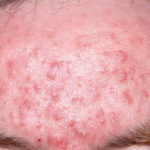 ,
,  ,
,