Date: 26 November 2013
Further image details
Image A. Long standing sarcoidosis, on corticosteroids with fibrosis and cavitary disease, and a possible fungal ball in the cavity on the left (1996).
Image B. Long standing sarcoidosis, on corticosteroids with 2 cavities containing aspergillomas, one on the left and one on the right (1996).
Image C. Sarcoidosis with progressive cavity formation and aspergillomas. Probable CIPA given appearances (2000).
Image D. Sarcoidosis with progressive cavity formation and aspergillomas. Probable CIPA given appearances (2000).
Image E. Sarcoidosis with progressive cavity formation and aspergillomas. Probable CIPA given appearances (2000).
Copyright: n/a
Notes: n/a
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
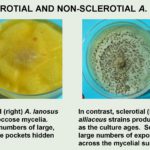
Sclerotial strains produce bright yellow, floccose mycelia. Sclerotial strains produce small numbers of large, fused sclerotial bodies in discrete pockets hidden within the mycelium.

-
Aspergillus alliaceus. No branching was observed in A. alliaceus conidiophores. Sclerotial strains typically produce large numbers of exposed, uniformly-shaped sclerotia across the mycelial surface.

-
Aspergillus alliaceus – Sclerotial. A. alliaceus strains produce flat, pale mycelia that darken as the culture ages.Sclerotial strains typically produce large numbers of exposed, uniformly-shaped sclerotia across the mycelial surface.

-
A. alliaceus strains produce flat, pale mycelia that darken as the culture ages.Sclerotial strains typically produce large numbers of exposed, uniformly-shaped sclerotia across the mycelial surface.