Date: 6 June 2023
Copyright:
Wang H, Lu Z, Qu HJ, Liu P, Miao C, Zhu T, Li J, Hong K, Zhu W. Antimicrobial aflatoxins from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus flavus 092008. Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Aug;35(8):1387-92. doi: 10.1007/s12272-012-0808-1. Epub 2012 Sep 1. PMID: 22941481.
Notes:
Structure of Aflatoxin B2b
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Mucous plug examined by light microscopy with KOH, showing a network of hyaline branching hyphae typical of Aspergillus, from a patient with ABPA.

-
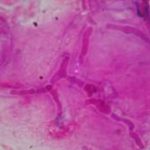
Corneal scraping stained with lactophenol cotton blue showing beaded septate hyphae not typical of either Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp, being more consistent with a dematiceous (ie brown coloured) fungus
-
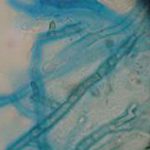
Corneal scrape with lactophenol cotton blue shows separate hyphae with Fusarium spp or Aspergillus spp.
-
A filamentous fungus in the CSF of a patient with meningitis that grew Candida albicans in culture subsequently.

-
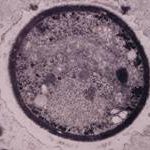
Transmission electron micrograph of a C. neoformans cell seen in CSF in an AIDS patients with remarkably little capsule present. These cells may be mistaken for lymphocytes.
-
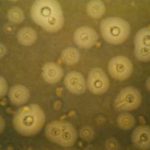
India ink preparation of CSF showing multiple yeasts with large capsules, and narrow buds to smaller daughter cells, typical of C. neoformans
-
PAS stain. An example of Aspergillus fumigatus.
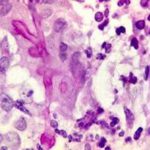
(PAS-stained) in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease showing a 45 degree branching hypha within a giant cell. Rather bulbous hyphal ends are also seem, which is sometimes found inAspergillus spp. infections, histologically. (x800)