Date: 26 November 2013
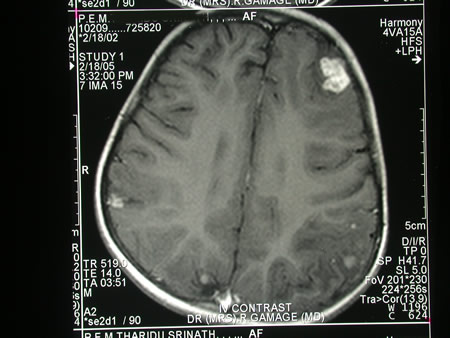
Image c. 3 yr old boy with CNS aspergillosis pt TS. MRI scan pre-amphotericin B
Copyright: n/a
Notes:
A 3 year old boy, quite active and healthy clinically, who has CNS aspergillosis. He was first seen about 4 months ago for a red eye, which turned out to be panophthalmitis; culture yielded Aspergillus spp. He received 2 weeks of iv amphotericin and was sent home by the ophthalmologists. No h/o eye trauma. He returned 2 weeks ago with focal fits, and the MR showed several lesions bilaterally (including ring enhancing lesions) and normal sinuses, and a brain bx showed fungal hyphae (no culture this time). His immune status (normal WCC and neutrophil function so far) was investigated.
He was given conventional amphotericin for 8 weeks, and switched to oral itraconazole. We had to limit the ampho to 0.7 mg/kg owing to toxicity (mainly hypokalaemia).
The MRI scan was repeated at about 6 weeks, and generally showed good improvement (scans e-h). The enhancement/flare were gone but remained in a few lesions, the lesions themselves were all either gone or much smaller. Further investigations revealed the child was immunocompetent.
Patient was switched from amphotericin to oral itraconazole at week 8 essentially on a clinical assessment. Awaiting follow-up.
Images library
-
Title
Legend
-
Image a. 3 yr old boy with CNS aspergillosis pt TS. MRI scan pre-amphotericin B
-
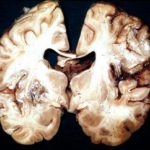
Section though unfixed brain showing large pale area of infarction deep in the parietal cortex, in which Aspergillus hyphae were seen histologically. The patient developed disseminated aspergillosis after a prolonged stay in intensive care after contracting severe community acquired pneumonia.
-
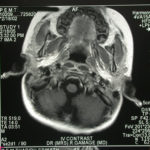
The woman had received a renal transplant several months prior to developing a stroke with reduced consciousness. The enhanced CT scan of her brain showed multiple ring-enhancing lesions bilaterally with little surrounding oedema. Biopsy confirmed invasive aspergillosis on histology and culture.
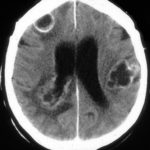
-
Further details
Image A. Multiple ring enhancing abscesses with substantial surrounding oedema was demonstrated. He had no focal neurological deficits. A needle aspiration confirmed the clinical impression of cerebral aspergillosis by culture and microscopy.
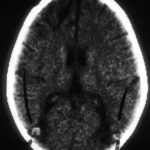
Image B. Resolution of cerebral aspergillosis, pt MN. Focal scars with some surrounding oedema are seen in the site of the prior abscesses.
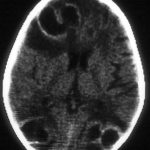 ,
, 
-
Contrast enhanced CT scan of the brain showing unequivocally 2 hypodense lesions, one in the left basal ganglia and one in the right occipital cortex. There is the possibility of another smaller left sided occiptal cortex. These lesions do not have the appearance of abscesses, but rather of ischaema.

-
Unenhanced CT scan of the brain in an allogeneic bone marrow transplant recipient demonstrating a large, variably hypodense lesion in the area of the left basal ganglia and possible additional lesions in the posterior parietal and/or occipital cortex.
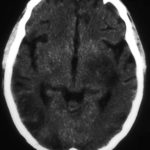
-
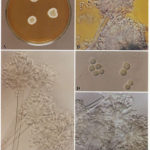
A. versicolor by microscopy showing very long thin conidiophores.

-
Pigmentation of Aspergillus versicolor colonies ranged from pale green to greenish-beige, pink-green, dark green and brown. Reverse is usually reddish. The growth rate is usually slow. Cultured on Sabouraud dextrose agar with chloramphenicol.

-
A Colonies on MEA after one week; B, C conidial heads with tip of conidiophire, x920; D conidial head, x 2330; E conidial heads x920
-
Cultures were grown on malt extract agar. Image kindly provided by Niall Hamilton.