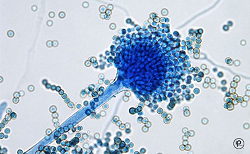
Description:
Although people usually relate fungi with diseases, Dr. Anne Pringle provides an overview of the vastly diverse and complex world of fungi, and provides examples of the beneficial roles that fungi have on Earth. For example, although some fungi have been associated with devastating infections that threaten harvests every year, other fungi are mutualists needed for the healthy development of plants and animals.
In her second lecture, Pringle explains how one can use a “reverse ecology” approach to describe and characterize different organisms and their habitats, by studying their genes. Her laboratory used this approach to study the origins of the Bay Area Amanita phalloides. Although Amanita phalloides was thought to be an invasive species, historical records were mostly descriptive and hard to use as concrete evidence of the species’ biogeography. Using genetic information, the Pringle laboratory was able to definitively prove that early samples identified as Amanita phalloides in the US are distinct from the European species. They also used molecular data to document the symbiotic associations between Amanita phalloides and plants, proving the efficacy of these approaches to study species that are hard to grow in the lab.
In her third lecture, Pringle provides an overview of convergent interactions, defined as the independent emergence of multi-species interactions with similar physiological or ecological functions. For example, multiple plant lineages have independently evolved interactions with fungi in order to exchange resources and form what are known as mycorrhizal symbioses. To further understand how convergent interactions are formed, the Pringle laboratory studied the evolution of plants that have “pitcher”-like structures as well as the mycorrhizal symbiosis in the Amanitagenus.
Medical and Patient education videos
-
Title
Description
-

Stewart Armstrong has chronic pulmonary aspergillosis and has undertaken to record a video of every day of his life for a month in order to help raise awareness of aspergillosis and how it impacts their daily lives.
These videos are interesting for a number of reasons – not least because patients often say that they don’t look unwell so many people don’t understand how serious aspergillosis is. Does Stewart look or act unwell?
See the month of vlogs in the playlist below, or go to Stewart’s YouTube page to watch more of his videos.
-

Global fungal killers and life-threatening infections
Fungi are everywhere, and a few species can cause very serious lethal infections. Fungal infections
-

This panel considers and debates one of the greatest obstacles to food security in many parts of the world: mycotoxin. Aflatoxin is a particularly dangerous mycotoxin produced predominantly by two Aspergillus fungi. It colonizes a variety of important food and feed crops both pre- and post-harvest, including groundnuts, tree nuts, maize, rice, figs and other dried foods, spices, crude vegetable oils and cocoa. Contaminated crops have significant health risks for both humans and animals, having been linked to retarded growth and development (stunting), immunosuppression and liver cancer. The aflatoxin issue has other, complex implications for food security and, by limiting farmers’ access to international markets, can lead to food waste and economic instability.
Panelists:
-John Lamb, Principal Associate, Abt Associates
-Dr. Kitty Cardwell, National Program Leader, USDA-NIFA
-Barbara Stinson, Senior Partner, Meridian Institute; Project Director, Partnership for Aflatoxin Control in Africa
-Moderator: Dr. Howard-Yana Shapiro, Chief Agricultural Officer, Mars, Incorporated -

The role of poorly maintained ventilation ductwork in spreading airborne infections is largely ignored because it is ‘out of sight out of mind’, but recent analysis by healthcare professionals confirms that the risks are increasing.
Ghasson Shabha will identify particular threats in healthcare facilities from dirty ductwork. He also points out that fewer than 5% of building air-conditioning systems have been inspected despite regulations making this mandatory. Dr Shabha will look at how planned cleaning strategies can reduce risks and how hospitals can use 3D building information modelling software to identify ‘infection hotspots’.
The healthcare environment can be described as a reservoir for potentially infective agents which can spread unpredictably in a whole array of ways particularly in ventilation and air-conditioning systems making it difficult to effectively control and manage, for those seeking timely information about the patterns of cross-infection. The severity of the problem has been highlighted extensively over the past decade, as part of wider umbrella of what was known as health care acquired infections (HCAIs). Airborne transmission extends over a wide spectrum, and includes many prevalent agents, inter alia Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB),nosocomial MRSA, Aspergillus fumigatus, Serratia marcescens, norovirus, and other airborne infection.
Dr Shabha was speaking live from Birmingham and this CIBSE ASHRAE Group (cibseashrae.org) webinar was co-sponsored by the B&ES Ventilation Hygiene Group and the Institute of Healthcare Engineering and Estate Management (IHEEM).
-

Oliphant Science Awards – Year 1 project by Haruki Kurioka, Aleksa Novakovic and Bogdan Novakovic (St Andrew’s Primary School, Adelaide)
Food that we consume daily is rich in good bacteria and fungi. Yogurt, Yakult and Natto (fermented soybeans) are rich in bacteria. Cheeses (e.g. Brie & Blue cheese) and Koji contain fungi Penicillium and Aspergillus, respectively. Many Japanese and continental seasonings and dishes can be prepared with those products. Many kids and their parents don’t know much about good bacteria and fungi. First year students are here to tell us their story. Enjoy it!