Description:
Although people usually relate fungi with diseases, Dr. Anne Pringle provides an overview of the vastly diverse and complex world of fungi, and provides examples of the beneficial roles that fungi have on Earth. For example, although some fungi have been associated with devastating infections that threaten harvests every year, other fungi are mutualists needed for the healthy development of plants and animals.
In her second lecture, Pringle explains how one can use a “reverse ecology” approach to describe and characterize different organisms and their habitats, by studying their genes. Her laboratory used this approach to study the origins of the Bay Area Amanita phalloides. Although Amanita phalloides was thought to be an invasive species, historical records were mostly descriptive and hard to use as concrete evidence of the species’ biogeography. Using genetic information, the Pringle laboratory was able to definitively prove that early samples identified as Amanita phalloides in the US are distinct from the European species. They also used molecular data to document the symbiotic associations between Amanita phalloides and plants, proving the efficacy of these approaches to study species that are hard to grow in the lab.
In her third lecture, Pringle provides an overview of convergent interactions, defined as the independent emergence of multi-species interactions with similar physiological or ecological functions. For example, multiple plant lineages have independently evolved interactions with fungi in order to exchange resources and form what are known as mycorrhizal symbioses. To further understand how convergent interactions are formed, the Pringle laboratory studied the evolution of plants that have “pitcher”-like structures as well as the mycorrhizal symbiosis in the Amanitagenus.
Medical and Patient education videos
-
Title
Description
-
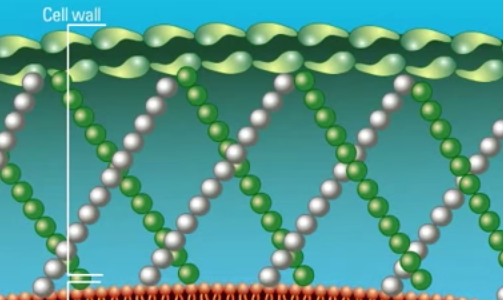
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane. Watch this animation for more information.
-

Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and are not related to bacteria. As eukaryotes, they contain membrane bound organelles and possess a cell membrane surrounded by a rigid cell wall. Watch this animation for more information on the unique structural properties of fungi.
-
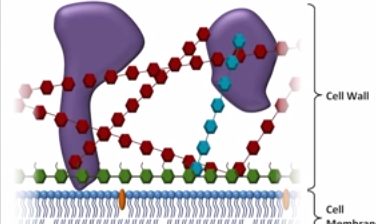
A review of antifungals, focusing on amphotericin B, azoles, and echinocandins. Structure, mechanism, spectrum of antifungal activity, common clinical uses, and common side effects/toxicities are all discussed. (April 2015)
-
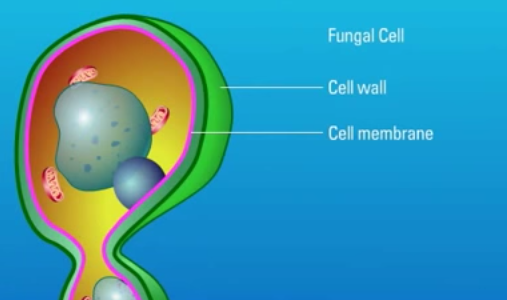
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
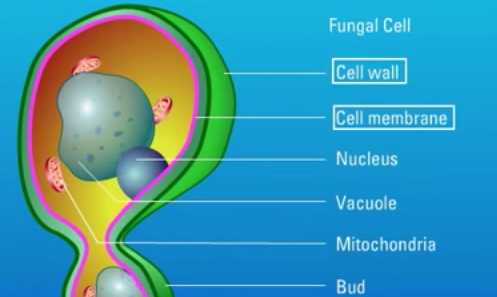
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
