Lecture Overview
In his first lecture, Dustin explains that adaptive immunity allows an individual to specifically recognize and respond to a vast number of molecules. B cells recognize intact antigens and produce neutralizing antibodies. T cells, on the other hand, have receptors on their surface that recognize very small antigen fragments bound to MHC on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APC). Dustin explains that T cells overcome the challenges of finding and binding to the APCs with the help of a multitude of adhesion molecules. Once the T cell receptor has bound a peptide antigen, an immunological synapse, with its typical bulls-eye structure, is formed resulting in T cell activation.
In Part 2, Dustin describes how a reconstituted system has allowed the immunological synapse to be studied in molecular detail. It is possible to visualize the localization of signaling molecules such as kinases, and determine the role of the actin cytoskeleton in regulating this localization. Dustin also touches on the role of the immunological synapse in autoimmune disease and cancer.
In his last lecture, Dustin presents work from his lab showing that T cell receptor enriched vesicles are generated in the immunological synapse. These vesicles can be transferred to B cells leading to activation of the B cells and, potentially, the production of higher specificity antibodies.
Speaker Bio
Michael Dustin is Professor of Immunology and Director of Research at The Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology at the University of Oxford. Prior to joining the Kennedy Institute, Dustin was a faculty member at the Skirball Institute of Biomolecular Medicine at New York University from 2001-2013 and at Washington University School of Medicine from 1993-2000. Dustin received his BA in Biology from Boston University and his PhD in Cell and Developmental Biology from Harvard University. As described in his iBioSeminar, Dustin’s lab studies the molecular events that take place at the immunological synapse. Future research will focus on developing therapies targeted to the immunological synapse to cure chronic inflammatory illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis. Dustin is an active participant in the immunology community; he is a member of numerous grant review committees and journal editorial boards. His research has been recognized with many awards including the 2000 Presidential Early Career Award in Science and Engineering and the 2012 DART-NYU Biotechnology Achievement Award.
Medical and Patient education videos
-
Title
Description
-
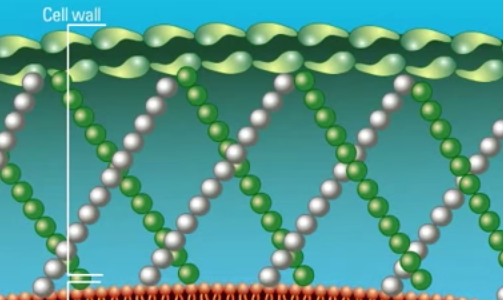
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane. Watch this animation for more information.
-

Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and are not related to bacteria. As eukaryotes, they contain membrane bound organelles and possess a cell membrane surrounded by a rigid cell wall. Watch this animation for more information on the unique structural properties of fungi.
-
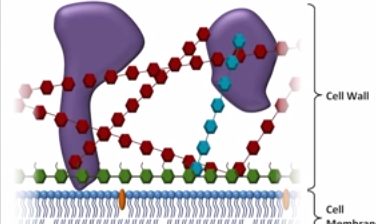
A review of antifungals, focusing on amphotericin B, azoles, and echinocandins. Structure, mechanism, spectrum of antifungal activity, common clinical uses, and common side effects/toxicities are all discussed. (April 2015)
-
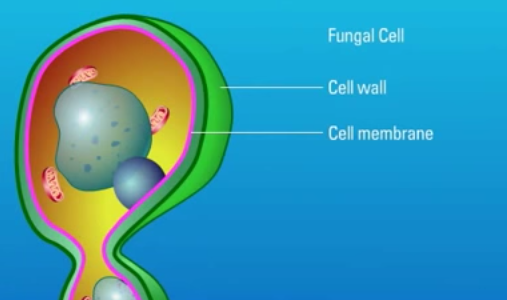
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
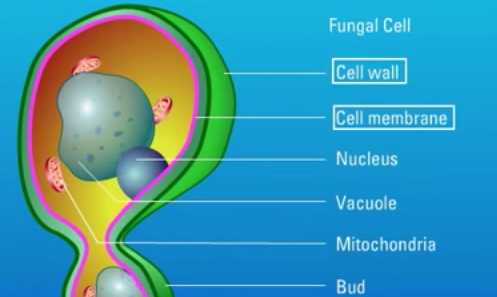
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
