Description: Selective Plane Illumination Microscopy (SPIM) greatly reduces phototoxicity in comparison with other fluorescent imaging modalities and makes it possible to image living small animals in 3D over extended periods of time. This talk describes an extension of SPIM such that it can be used with specimens on a coverslip rather than in a capillary (inverted SPIM or iSPIM), and a second modification that images the specimen using two perpendicular light sheets (Dual-View iSPIM or diSPIM), resulting in 3D datasets with the same resolution in X, Y, and Z (isotropic resolution)
About the Speaker: Hari Shroff
Hari Shroff is an Investigator at the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering at the National Institutes of Health. During his post-doc, which was with Eric Betzig at HHMI’s Janelia Farm Research Campus, he focused on the development of PALM (photoactivated localization microscopy) microscopy. Since then he has developed several microscopy techniques, such as diSPIM and instant structured illumination microscopy.
For full tutorial & assessment go to iBiology
Medical and Patient education videos
-
Title
Description
-

Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. The echinocandin class of antifungal agents target the cell wall of fungi. Watch this animation for more information.
-
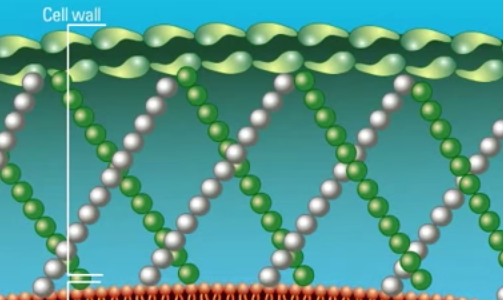
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane. Watch this animation for more information.
-

Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and are not related to bacteria. As eukaryotes, they contain membrane bound organelles and possess a cell membrane surrounded by a rigid cell wall. Watch this animation for more information on the unique structural properties of fungi.
-
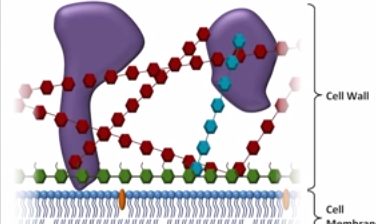
A review of antifungals, focusing on amphotericin B, azoles, and echinocandins. Structure, mechanism, spectrum of antifungal activity, common clinical uses, and common side effects/toxicities are all discussed. (April 2015)
-
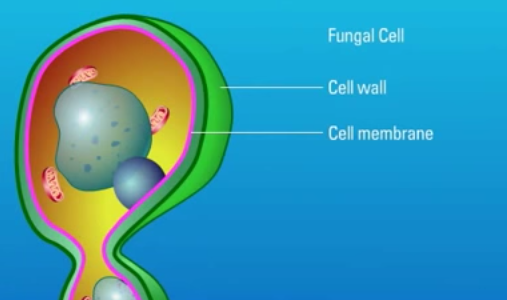
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
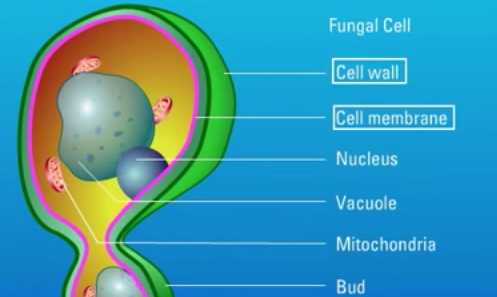
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms which possess a unique cell wall and cell membrane that can serve as targets for antifungal agents. Polyene antifungal agents such as Amphotericin B target the fungal cell membrane.
-
Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
-

Healthy Buildings 2015 Europe – Eindhoven, The Netherlands
