ID: 9
Medically significant: yes
Classification agreed: y
Contentious not verified: n
In ncbi taxonomy database: y
Available from atcc: y
CBS: y
Previous CBS: unknown
Sexual CBS: unknown
Contentious name: unknown
Previous name, contentious name: unknown
Sexual form exists: unknown
Sexual form contentious name: n
Sexual form in ncbi taxonomy database: n
Previous name in NCBI taxonomy database: n
Previous name available at ATCC: unknown
Reference (original paper):
Desmazières, J.B.H.J. 1834. Descriptions et figures de six hyphomycètes inédites à ajouter à la flore Française. Annales des Sciences Naturelles Botanique. 2:69-73
Medical significance update: The First Case of Total Dystrophic Onychomycosis Caused by Aspergillus clavatus Resistant to Antifungal Drugs. Falahati M, Ghojoghi A, Abastabar M, Ghasemi Z, Farahyar S, Roudbary M, Hedayati MT, Armaki MT, Hoseinnejad A. Mycopathologia. 2016 Apr;181(3-4):273-7. doi: 10.1007/s11046-015-9954-6.
Taxonomic family: Fungi, Ascomycota, Pezizomycotina, Eurotiomycetes, Eurotiomycetidae, Eurotiales, Trichocomaceae, Aspergillus
Species images:
-
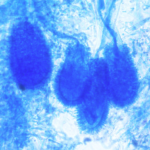
A Colonies on MEA after one week;B conidial heads and tip of conidiophore, x 230; C conidial head, x920; E conidial head, x920. Copyright B.Flannigan, R Samson & JD Miller (From Microorganisms in home and indoor work environments, Published by Taylor and Francis)

-
microscopic characters Conidiophore stipes(C)1300-2800um long:Vesicles(V)40-70um wide,clavate:Phialides(Ph) uniseriate:Conidia(Con)3.5-4.0um long,smooth walled.

-
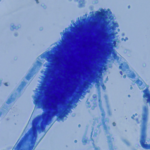
growing on contaminated barley malt. The deep blue-green heads made up of chains of conidia are seen on the left. On the right, conidiophores from which conidial chains are developed show typical clavate heads. Stain- Cotton blue in Lactophenol.

-
Left= an agar air plate exposed for 2 minutes after the barley had been turned. showing numerous colonies of the fungus following incubation at 26C on 2% malt agar.Right= A sputum sample taken from a maltworker after exposure showing many fungal colonies when cultured on agar. His commensal yeast flora is seen towards the right base as cream/white colonies.

Currently accepted name (anamorph): A. clavatus
Index Fungorum: Link
Mycobank: Link
Taxonomic family: Fungi, Ascomycota, Pezizomycotina, Eurotiomycetes, Eurotiomycetidae, Eurotiales, Trichocomaceae, Aspergillus
Computed content type (Species): Species
Species
-
Title
Author
Medically significant
Mycobank
Index fungorum
-
Muntañola-Cvetkovic, M.; Bata, J. 1964. Some species of Aspergillus from Yugoslavia. I. Bulletin de l’Institut et du Jardin Botaniques de l’Université de Beograd. 1:181-212
no
-
Stolk, A.C. 1954. Aspergillus asperescens n.sp. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 20(3):299-304
no
-
Bartoli, A.; Maggi, O. 1978. Four new species of Aspergillus from Ivory Coast soil. Transactions of the British Mycological Society. 71(3):383-394
no
-
Samson, R.A. 1979. A compilation of the Aspergilli described since 1965. Studies in Mycology. 18:1-40
no
-
Sappa, F. 1955. Nuove specie di Aspergillus dei terreni della savana spinosa somala. Allionia. 2(2):247-257
no
-
Mehrotra, B.S.; Agnihotri, V.P. 1962. Two new species of Aspergillus from India. Mycologia. 54(4):400-406
no
-
Samson, R.A.; Mouchacca, J. 1975. Additional notes on species of Aspergillus, Eurotium and Emericella from Egyptian desert soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 41(3):348
no

 ,
,  ,
,