ID 2: CAS Registry Number 1116153-15-1
Toxin: unknown
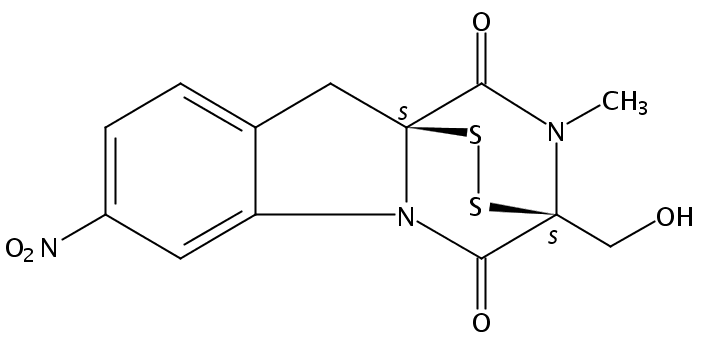
Trivial name:
Glionitrin A
Systematic name:
10H-3,10a-Epidithiopyrazino[1,2-a]indole-1,4-dione, 2,3-dihydro-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-7-nitro-, (3S,10aS)-
Molecular formulae:
C13 H11 N3 O5 S2
Molecular weight: 353.37
Chemical abstract number: CAS Registry Number 1116153-15-1
References URL:
Aspergillus Species known to produce this metabolite:
History:
In a recent study, we isolated the diketopiperazine disulfide glionitrin A from the co-culture broth of a mine drainage-derived fungus (Aspergillus fumigatus KMC901) and bacterium (Sphingomonas KMK001). Here, we investigated the antitumor activity of glionitrin A and its underlying molecular mechanisms in human prostate cancer DU145 cells. Glionitrin A showed significant cytotoxicity, promoting cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Glionitrin A-treated cells exhibited elevated levels of phospho-histone 2AX (Ser139), a marker of DNA damage, and accumulated in both S phase and G2/M phase due to the activation of checkpoints associated with the ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated and ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated-Rad3-related Chk1/2 pathway downstream of p53-binding protein 1 phosphorylation at Ser1778. In addition, glionitrin A induced apoptosis through both caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Glionitrin A activated caspase-8, -9 and -3 and also released endonuclease G from the mitochondria to the nucleus in a dose-dependent manner. Our in vivo study performed in nude mice bearing xenografts of DU145 cells showed that glionitrin A dramatically reduced the tumor volume by an average of 38.2% (5 mg/kg, per os (p.o.)) and 71.3% (10 mg/kg, p.o.) at 27 d after the beginning of treatment. Taken together, these findings provide a detailed description of the mechanism underlying the biological activity of the new natural product glionitrin A, which has the potential to be developed as an anti-prostate cancer agent.
Structure image:
Mycotoxin & Metabolites
Mycotoxin & Metabolite database
Aspergillus species produce a large number of secondary metabolites, sometimes referred to as extrolites. We attempt to list them all here and we also collect published papers.
