ID 2: 475
Toxin: y
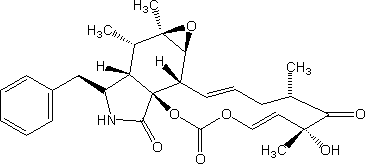
Trivial name:
21,23-Dioxa[13]cytochalasa-13,19-diene-1,17,22-trione, 6,7-epoxy-18-hydroxy-16,18-dimethyl-10-phenyl-, (7S,13E,16S,18R,19E)-; Cytochalasin E; NSC 175151; [1,3]Dioxacyclotridecino[4,5-d]oxireno[f]isoindole-5,10,12(4H,6H)-trione, 3,13,14,14a,15,15a,16a,16b-octahydro-6-hydroxy-4,6,15,15a-tetramethyl-14-(phenylmethyl)-, [4S-(1E,4R*,6S*,7E,11aR*,14R*,14aR*,15R*,15aS*,16aR*,16bR*)]-
Systematic name:
14-Benzyl-6-hydroxy-4,6,15,15a-tetramethyl-3,13,14,14a,15,15a,16a,16b-octahydro[1,3]dioxacyclotridecino[4,5-d]oxireno[2,3-f]isoindole-5,10,12(4H,6H)-trione
Molecular formulae:
C28H33NO7
Molecular weight: 495.57
Chemical abstract number: 36011-19-5
Chemical type: Alkaloid
Literature reference:
References URL:
Aspergillus Species known to produce this metabolite:
Toxicity:
The cytochalasins inhibit cleavage in cultured animal cells leading to the formation of multinucleated cells and cells without nuclei. Cytochalasin E is one of the most acutely toxic of the group causing necrosis of many body organs and pulmonary haemorrhage. Oral LD50 in rats 9.1 mg/kg body-weight.
Structure image:
Date uploaded: 2005-12-13 00:00:00
Mycotoxin & Metabolites
-
Metabolite
Produced by (species)
Molecular weight
References
-
399.0
428.5
445.5
443.5
321.5
138.1
264.3
138.1
182.2
Mycotoxin & Metabolite database
Aspergillus species produce a large number of secondary metabolites, sometimes referred to as extrolites. We attempt to list them all here and we also collect published papers.
Search Metabolite papers here
