Submitted by helenfindon on 3 June 2019
This large, population based study estimates the prevalence of severe asthma according to the three internationally well-known criteria: the ATS workshop definition from 2000 used in the US Severe Asthma Research Program (SARP), the 2014 ATS/ERS Task force definition and GINA 2017 (Global Initiative for Asthma).
It reports on the incidence of severe asthma in an adult population based cohort (1006 participants) who were diagnosed between 1986 and 2001.
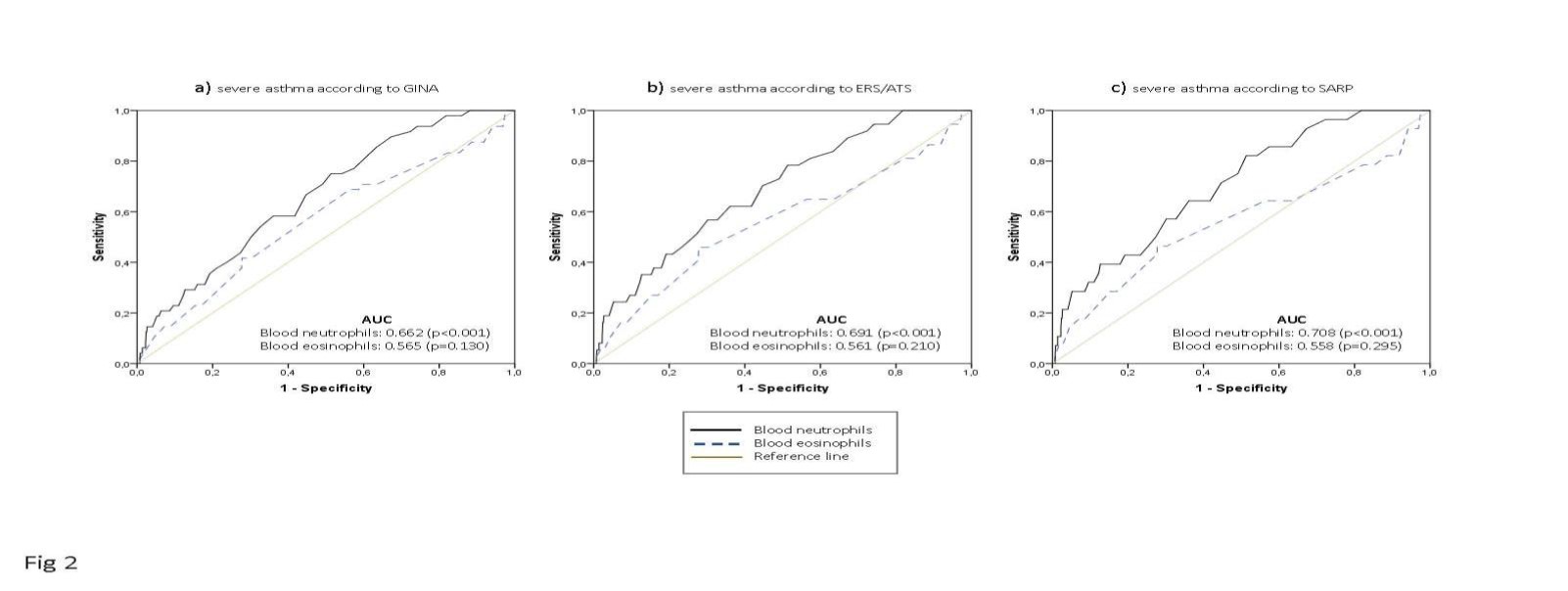
The prevalence of severe asthma among all patients with current asthma was 3.6%, 4.8% and 6.1%, according to the SARP-, ERS/ATS- and GINA-definitions, respectively. Interestingly, two distinct types of asthma were detected, one of which was severe asthma with sensitization to moulds, particularly Aspergillus.
The prevalence of sensitization to Aspergillus in individuals with severe asthma was 10%, 12.8% and 17.2%, according to the SARP, ERS/ATS and GINA definitions, respectively, compared to 2.1% in individuals with ‘other’ i.e. non-severe asthma.
News archives
Showing 10 posts of 953 posts found.
-
Title
Date