Submitted by GAtherton on 16 November 2016
The National Aspergillosis Centre & Manchester Academy Health Science Centre have published a new report estimating the numbers of people living with fungal disease. The last UK figures were released in 2006 by the Health Protection Agency and largely referred to cases in 2002, the new figures relate to years since 2010.
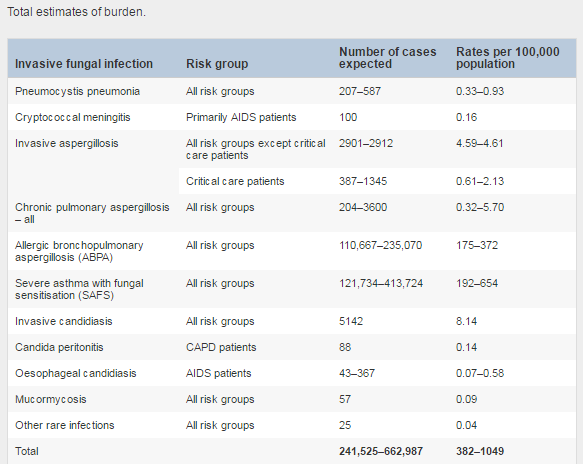
The new figures feature all known fungal infections but most prominent amongst those numerically are those for Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) and Severe Asthma with Fungal Sensitivity (SAFS) which are estimated to consist of up to 235, 000 and 413, 000 cases each respectively – a significant increase on earlier estimates. This report is the first attempt to calculate numbers for SAFS, a subgroup of asthma that are particularly severe cases with poor control and require steroid inhalers to control. Encouraging recognition of this group is important as many in this group (70-80%) are known to respond positively to oral antifungal medication and few are prescribed those drugs.
It is also worth highlighting that there are thought to be increasing rates of infection and in antifungal drug resistance in pathogenic fungal species.
Report author Professor Denning (Director of the National Aspergillosis Centre at the University Hospital of South Manchester) commented:
“While the UK is rich in data sources, there is a remarkable poverty of contemporary studies of fungal diseases. An accurate estimate of total burden will ultimately rely on improved diagnostic testing and laboratory reporting”.
“This report gets us closer to true burden of fungal diseases in the UK – necessary for improved diagnosis and reducing death. The scale of the ‘fungal asthma’ problem is staggering, and potentially remediable with antifungal therapy, as I know from treating hundreds of affected patients,”.
News archives
-
Title
Date