Submitted by GAtherton on 21 March 2017
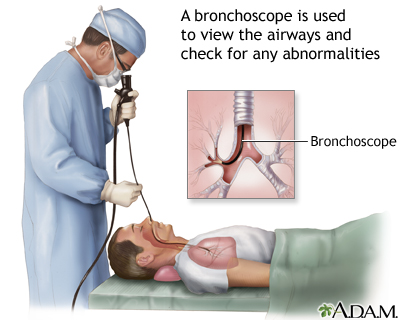
A clinical research group in New Delhi, India have tested the efficacy of bronchial instillation (i.e. the direct instillation of voriconazole solution into a lung region affected by haemoptysis and aspergilloma by passing a bronchoscope into the lungs via the mouth) and have published very positive results.
The group took 82 patients with pulomonary aspergilloma after TB who had had very significant haemoptysis ranging from <200ml/day to more than 600ml/day and an aspergilloma (average size 4.5cm). The patients had been treated with tranexamic acid and embolisation as is standard practice.
Voriconazole tablets were dissolved in saline and each patient was give 4 instillations into the lung area affected by bleeding and aspergilloma.
After instillation of voriconazole over half had a reduced size of aspergilloma and almost all (95%) had at least some degree of successfully controlled haemoptysis – 69 patients had previously had severe or massive bleeding. The mean time interval before their next significant haemoptysis was 25 months whereas prior to instillation it was 8 months.
Instillation with antifungal drugs has been tried before but on small numbers of patients and with amphotericin rather than an azole drug that would have activity against Aspergillus. Results were mixed and patients found the procedure difficult to tolerate. In this study the authors recorded little bronchospasm with 46% coughing during or after the procedure.
The apparent safety and efficacy of this procedure offers encouragement that after some assessment we will be able to offer a new technique to many patients suffering from even massive haemoptysis
News archives
-
Title
Date